表达式语言(SpEL)
Spring 表达式语言(SpEL)支持在运行时查询和操作对象。本篇文章我们来学习,如何使用SpEL,并简单介绍下,他在IoC容器中,扮演什么角色。
SpEL 使用#
首先我来看一张类图,图中红框标注的是SpEL中重要的角色(接口)。
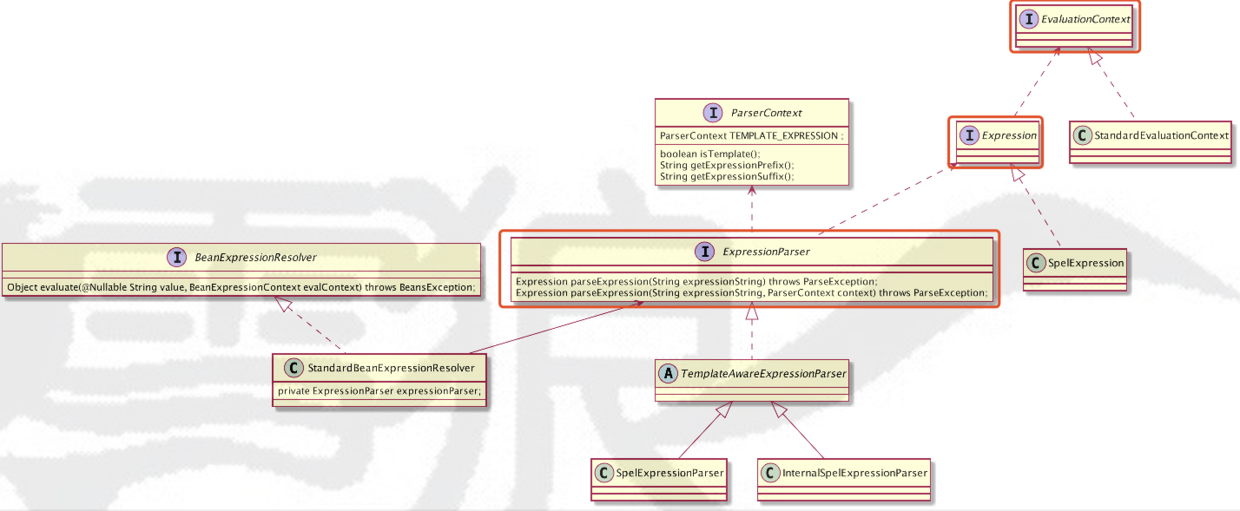 接着我们来看看Spring 源码
接着我们来看看Spring 源码org.springframework.expression.spel.spelExpressionMapWithVariables中一个测试例子
@Test@SuppressWarnings("serial")public void spelExpressionMapWithVariables() { // (1) 创建一个解析器对象 ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser(); // (2) 解析一个表达式对象 Expression spelExpression = parser.parseExpression("#aMap['one'] eq 1"); // (3) 提供一个表达式运行环境 StandardEvaluationContext ctx = new StandardEvaluationContext(); ctx.setVariables(new HashMap<String, Object>() { { put("aMap", new HashMap<String, Integer>() { { put("one", 1); put("two", 2); put("three", 3); } });
} }); // (4) 执行表达式 boolean result = spelExpression.getValue(ctx, Boolean.class); assertTrue(result);
}可以看到当我们需要使用SpEL时,需要有这几步操作
- (1) 创建一个解析器对象
- (2) 解析一个表达式对象
- (3) 提供一个表达式运行环境
- (4) 执行表达式
这里我们重点讲一下(2),我们在来看一张图,这是官网列举的SpEL所支持的表达式。
 我们挑选几个来讲解一下,(其它的老铁们可以戳我看详细)
我们挑选几个来讲解一下,(其它的老铁们可以戳我看详细)
案例代码#
创建parse对象
SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();class A{ public static int plus(Integer one,Integer two){ return one + two; }}定义表达式执行上下文
EvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadOnlyDataBinding().build();Method plus = A.class.getDeclaredMethod("plus",Integer.class,Integer.class);解析List#
解析字符串为List
List list = (List) parser.parseExpression("{1,2,3,4,'g'}").getValue();List<Map> listMap = (List) parser.parseExpression("{{age:1},{age:2},{age:3}}").getValue();解析Maps#
解析字符串为Map
Map map = (Map) parser.parseExpression("{name:'lykos',age:18}").getValue();解析Functions#
解析执行方法,这里需要注意#plus,当我们需要引用变量时需要加#号
context.setVariable("plus",plus);int plusResult = (Integer) parser.parseExpression("#plus(3,4)").getValue(context);Expression templating#
模板表达式,这里需要注意的是,我们需要定义模板格式,也就是需要告知解析器哪些是需要解析成表达式的,这个格式定义需要实现ParseContext接口,ParserContext.TEMPLATE_EXPRESSION是Spring提供的默认格式(表达式需要用#{expression})
String plusResult = (String) parser.parseExpression("3 plus 4 is #{#plus(3,4)}", ParserContext.TEMPLATE_EXPRESSION).getValue(context);String plusResult2 = (String) parser.parseExpression("custom parsercontext 3 plus 4 is $[#plus(3,4)]", new ParserContext() { @Override public boolean isTemplate() { return true; } //前缀字符 @Override public String getExpressionPrefix() { return "$["; } //后缀字符 @Override public String getExpressionSuffix() { return "]"; }}).getValue(context);SpEL 在IoC容器中使用#
Spring 容器中也是支持SpEL的。因为在AbstractApplicationContext.prepareBeanFactory方法中会添加BeanExpressionResolver(Bean定义的表达式解析接口)对象值,BeanExpressionResolver本身是一个接口,定义如下,其主要作用就是根据一个表达式解析出对象。他的实现类是StandardBeanExpressionResolver
public interface BeanExpressionResolver { Object evaluate(@Nullable String value, BeanExpressionContext evalContext) throws BeansException;}StandardBeanExpressionResolver内部是包装了ExpressionParser对象,我们在看看evaluate的实现,可以确定的是StandardBeanExpressionResolver对象解析也是使用了SpEL。
public Object evaluate(@Nullable String value, BeanExpressionContext evalContext) throws BeansException { if (!StringUtils.hasLength(value)) { return value; } try { Expression expr = this.expressionCache.get(value); if (expr == null) { expr = this.expressionParser.parseExpression(value, this.beanExpressionParserContext); this.expressionCache.put(value, expr); } StandardEvaluationContext sec = this.evaluationCache.get(evalContext); if (sec == null) { sec = new StandardEvaluationContext(evalContext); sec.addPropertyAccessor(new BeanExpressionContextAccessor()); sec.addPropertyAccessor(new BeanFactoryAccessor()); sec.addPropertyAccessor(new MapAccessor()); sec.addPropertyAccessor(new EnvironmentAccessor()); sec.setBeanResolver(new BeanFactoryResolver(evalContext.getBeanFactory())); sec.setTypeLocator(new StandardTypeLocator(evalContext.getBeanFactory().getBeanClassLoader())); ConversionService conversionService = evalContext.getBeanFactory().getConversionService(); if (conversionService != null) { sec.setTypeConverter(new StandardTypeConverter(conversionService)); } customizeEvaluationContext(sec); this.evaluationCache.put(evalContext, sec); } return expr.getValue(sec); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanExpressionException("Expression parsing failed", ex); }}还记得@Value这个注解么,我们经常用他来对我们的属性赋值,如下
@Value("name")private String name;
@Value("#{b.age}")private String name;
@Value("${name}")private String name;@Value("name")#
是直接给变量赋name值
@Value("#{b.age}")#
是获取容器中b对象age属性值
@Value("${name}")#
是获取配置文件中name值